A Vertical Electrical Sounding Application for Groundwater Search in Qinhai
Abstract: Briefly introduced in this paper are the variety of patterns of resistivity sounding curves for various kinds of terrain conditions in Qinghai,along with distributive features of resistivity and chargeability for aquifer.It is emphasized that optimal combination of electrical methods and reasonable electrode—configuration are the key points for getting expected results. and some hydro geological factors unfavorable for laying out drilling based on geophycal data are also discussed for different terrain conditions.
Key words: optimization of method combination, pattern of resistivity corves, electrical characteristics of aquifer, dry hole.
0, Introduction
Qinghai is an inland plateau where lack the water shortage; in some places; the water is the key point to improve the lives of people. Therefore, actively seeking groundwater resources to improve local people's living has an important practical significance.
1, methods and techniques to find water
Main methods to find water is resistivity sounding method, time domain induced polarization, resistivity profile, IP profile and electrical logging method. VES array mainly are symmetrical four-pole, three poles, three pole of fixed point, five poles, profiling devices are intermediate gradient, and high density imaging. The main instrument in survey is WDJD-4 series Resistivity/IP instrument.
2, analyses of results
2.1 water detection in valley and tributaries
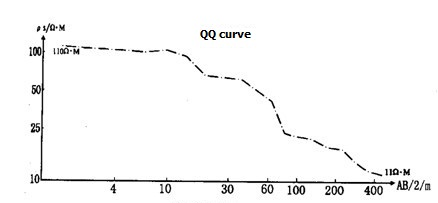
Quaternary deposits in the rock is mainly sandy gravel, sandy gravel and mud sand ; sub-basement is mainly the mudstone (E) and metamorphic rocks, etc.; the aquifer lithology is sandy gravel soil. The sounding curve in such landscapes generally is K, H, Q, KQ type, the aquifer electrical ρ = 100 ~ 300Ω.m, η = 1.5-2.5%. General speaking, the dramatic variation on the right branch on the KQ,Q curve means water level. According to KQ,Q curves, we can infer groundwater depth and thickness of the aquifer (Figure 1). The aquifer electrical characteristics in the vally and tributaries usually is the medium polarization and medium/high resistance.
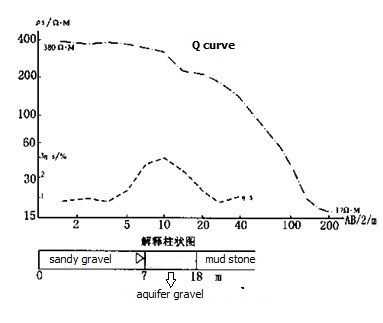
Figure 1
Qinghai Yellow River valley, Huangshui River Valley, Ho Mun Valley, Blue Valley and so are all the landforms above. To use electrical method to confirm the location of the well will be easy with small risk.
But in some base and old terrace, due to insufficient supply from the tributaries or much mud in aquifer, it will result in dry hole or few water.
2.2 Water detection in the mountain basin
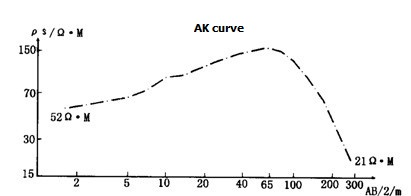
Quaternary deposits in Qinghai mountain basin is mainly fine gravel of fluvial-lacustrine deposits, fine sand, loam, etc.; the aquifer lithology is mainly fine sand layers. Some basin can form a confined aquifer. The VES curve is mainly QQ, KH, KQ type, the electrical properties of the aquifer ρ = 15 ~ 60Ω.m, ηS = 3 ~ 5%, the electrical characteristics of the aquifer is low resistivity and high polarizability (Figure 2).
Figure 2
Palit Basin, tea cards basin, Ulan Basin and Qinghai Lake basin in Qinghai region, according to the above electrical characteristics, are easy to confirm a higher well Electrical method. But in some areas around the basin, due to the uplift of basement structure and the mix of the alluvial materials, it is by easy to form Quaternary aquifer containing no water or weak hydrogeological phenomena (as Palit basin, tea cards Basin .)
2.3 water detection on foreland pluvial fan
Quaternary deposits of alluvial fan are mainly sediment gravel, boulder clay with gravel and sub-sand. This area features complex construction, uniform water zone and poor distribution. The sounding curves generally is K, KH, KQ type, the electrical properties of the aquifer ρ = 100 ~ 350Ω.m, ηS = 2 ~ 3%,. That is medium polarization and high resistance: the alluvial fan fringes sounding curves for the Q, H, A-type (Figure 3). Aquifer electrical ρ = 50 ~ 100Ω.m-1, ηS = 3 ~ 4%,, the middle-resistivity characteristics of heightened polarization.
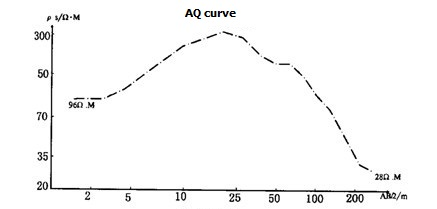
Figure 3
And at the transition zone or the center, the water level has a obvious exception in ρs, ηS , which is easy to analyze situation of water; but in the marginal zone, such exceptions are sometimes not obvious. At the edge of Qaidam Basin, some alluvial fan, because the aquifer particles become thinner or higher clay content, usually the well gush water small in center.
2.4 fresh water detection on salt-water area
In Qinghai lack, Chaka, Golmud and other inland basin of Qinghai, the specific sedimentary environment result in the mix of slat water layer and fresh water layer. The complex construction makes the fresh water detection very difficulty. Some basin show HK, AK curve means have fresh water at upper part and salt water at lower part.; while some shows A, AA curve means have fresh water at lower part, and salt water at upper part. If the fresh water layer is thin and very deep, it is hardly to judge.
Figure 4
In such are, electric method need to work with hydrologic logging method.
2.5 water detection on mountain
Because of the specific condition, the Qiannao Mountain are lack the water on the ground, so the Quatenary clay contain few water also. To develop the basic bedrock pore, fissure water is the solution for finding underground water.
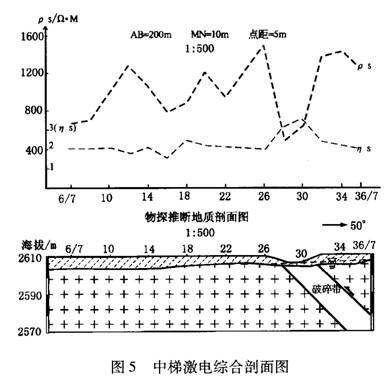
In the formation of Tertiary (E), Cretaceous (K) and others, the Res profile and curve of the aquifer sandstone, conglomerate layer show a abnormal high resistance with zigzag shape and some abnormal high polarizability. So it need other method to test at the same time as natural electric field method.
Figure 5 profile of middle gradient IP survey